Blogs
What is the secondary market?

The secondary market, often called the aftermarket, is a vital component of the financial ecosystem where investors buy and sell existing securities. Unlike the primary market, where securities are issued and sold for the first time, the secondary market allows the trading of already issued shares among investors.
As of January 2024, the market capitalization of NEPSE totaled Rs. 330,765.9 crores. About 23% of the total population of Nepal engages in the Stock market and the numbers keep growing.
The Secondary market is also known as NEPSE, Nepal Stock Exchange. It is the platform that allows you to buy or sell shares securely.
You may be interested in being a part of the 23% but may not know where to begin. This article can help you start your journey by telling you the basics of the secondary market.
What is the secondary market?
The secondary market serves as a platform where investors trade previously issued securities, such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives, without the involvement of the issuing companies. The shares bought in the primary market from the listed companies can be bought or sold here.
The prices of the shares differ from the original listed price. It depends on how the company is doing. If the company’s valuation has increased, it increases the cost per share, and similarly, if the company does not do well and its valuation has decreased, then the cost per share also decreases.
How can you enter the secondary market?
Apart from the basics that are required to be in the primary market like a bank account and opening a Demat account, you will also need the following additional accounts:
- Broker
- NEPSE TMS account
What is a broker account?
It is a standard practice that all the transactions done in the secondary market have to be done through a broker. You may wonder if you can buy or sell shares if you’ve already found a buyer or a seller. The answer is no. All of the buying and selling in NEPSE has to be done through a broker.
Brokers will receive a broker commission/fee which is a certain percentage of the amount transacted as a commission. You can create a broker account online or by visiting the broker’s office directly.
What is NEPSE TMS?
NEPSE TMS stands for Nepal Stock Exchange Trade Management System. After you have created your broker account, you can access NEPSE TMS. By filling in your username or client code and your password, you can trade in the secondary market from the comfort of your home.
The different brokers in the share market have their own unique TMS URLs. You can use it to come in contact with the broker you want.
To load money/collateral in the TMS account, you have to use connect IPS, Global IME, or Prabhu Bank digital wallet. Connect IPS links your bank account to your TMS account. These help you send a collateral amount to your TMS account. This allows you to buy and sell shares accordingly.
Functions of the Secondary Market
Providing Liquidity
One of the primary functions of the secondary market is to provide liquidity to investors by allowing them to buy and sell securities easily. Liquidity ensures that investors can convert their investments into cash quickly without notably affecting market prices.
Price Discovery
The secondary market facilitates price discovery by allowing investors to trade securities based on supply and demand dynamics. Through continuous trading activities, market prices are determined, reflecting the collective opinions and expectations of market participants.
Risk Management
Investors use the secondary market to manage their investment risks by diversifying their portfolios, hedging against price fluctuations, and adjusting their positions based on market conditions. The ability to trade securities freely provides investors with greater flexibility in managing their investment portfolios.
Challenges and Risks in the Secondary Market
Market Volatility
The secondary market is open to market volatility, characterized by rapid price fluctuations and unpredictable trading patterns. Volatility can be caused by various factors, including economic conditions, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment.
Insider Trading
Insider trading, where individuals trade securities based on non-public information, poses a significant risk to the integrity of the secondary market. Regulatory authorities enforce laws against insider trading to maintain market fairness and transparency.
Regulatory Changes
Changes in regulatory policies and market regulations can impact trading activities and investor behavior in the secondary market. Market participants need to stay informed about regulatory developments and adapt their strategies accordingly to mitigate regulatory risks.
The secondary market is where people earn a lot of profit. But it is also in the secondary market that people tend to lose money. It all depends on how good your research is and how alert you are to the happenings of the share market. Always remember, high risk equals high returns. It is a very lucrative market if you know where to invest and when to invest.
You may also like:
- What are the benefits of owning a share
- What are some common mistakes to avoid when trading stocks
- Basics to know before starting investment in Share Market
FAQs
What is TMS in stock trading?
TMS stands for Trading Management System. It allows the users to make transactions in the share market from their own homes. They can buy and sell shares from their own home.
What is the role of NEPSE in Nepal?
NEPSE shows the total market capitalization of companies’ transactions listed on the Nepal Stock Exchange.
Who owns NEPSE?
The government of Nepal owns NEPSE. The government owns 58.65% of the Nepal government.
How can I sell my stock in Nepal?
You can sell the stocks in Nepal in the secondary market by appointing a broker.
Who can invest in the share market?
Anyone with a trading account or an investment account can invest in the share market.
Blogs
Chhyangdi Hydropower Extends Deadline for Rights Share Application | Until 27th Ashad

The deadline for the ongoing rights share issue of Chhyangdi Hydropower Limited (CHL) has been officially extended until 27th Ashad, 2082. The issue had originally opened on 23rd Jestha, 2082, with an earlier closing date set for 12th Ashad, 2082.
Key Details of the Rights Share Issue
| Details | Information |
|---|---|
| Total Right Shares Issued | 3,869,775 units (1:1 ratio) |
| Face Value per Share | Rs. 100 |
| Total Issue Amount | Rs. 38.69 Crore |
| Current Paid-up Capital | Rs. 38.69 Crore |
| Post-Issue Paid-up Capital | Rs. 77.39 Crore |
As per the Central Depository System and Clearing Limited (CDSC), 23,503 applicants have applied for 2,317,902 units (worth Rs. 23.17 Crore) as of yesterday.
Eligibility and Application Process
Only those shareholders who held shares before the book closure date of 2nd Jestha, 2082, are eligible for this right share offering.
Interested shareholders can apply through:
- Global IME Capital Limited, Naxal, Kathmandu (Issue Manager)
- Designated branches of Global IME Bank Limited across Lamjung, including Besisahar, Sundarbazar, Bhulbhule, Siundibar, Udipur, and Dordhi
- Any C-ASBA-approved banks and financial institutions
- Online via “MeroShare”.
Applicants are advised to complete the process before banking hours on 27th Ashad, 2082 (Friday).
Important Note:
Payments must be made through an account payee cheque drawn in the name “GICL-BOK-CHHYANGDI RIGHT SHARE”, as per the instructions from Global IME Capital Ltd.
Contact Information
- Chhyangdi Hydropower Ltd
Phone: 977-01-4526483 / 4524925
Email: [email protected] | Website: www.chpl.com.np - Global IME Capital Ltd (Issue Manager)
Phone: 977-01-5970138
Email: [email protected] | Website: www.globalimecapital.com
Notice: Chhyangdi Hydropower Extends Deadline for Rights Share Application
Blogs
Election Commission Preparing to Announce By-Election Date | Voter Registration Now Open
The Election Commission of Nepal has begun preparations for by-elections to fill vacant positions at various levels of government. As part of this process, the Commission is urging all eligible Nepali citizens who have not yet registered their names in the voter list to do so immediately.
According to the Assistant Spokesperson of the Election Commission, Mr. Durga Prasad Chalise, individuals will not be allowed to register in the voter list once the election date is officially announced. Therefore, he emphasized the importance of early registration to avoid being left out.
The Election Commission recently held discussions with the Prime Minister, Mr. KP Sharma Oli, and the Acting Chief Election Commissioner, Mr. Ram Prasad Bhandari. They talked about setting a date for the by-elections. The main focus was on two key areas: Rupandehi Constituency No. 3 for the House of Representatives and Manang Province Assembly Constituency No. 1 (B). Elections in these regions are likely to be held in the second week of Kartik.
The position in Rupandehi became vacant after the passing of Rastriya Prajatantra Party MP Deepak Bohora. In Manang, the seat became empty after provincial assembly member Deepak Manange was sent to jail. In addition to these, more than a dozen ward chairman positions are also currently unoccupied in various local governments.
The Election Commission has issued a public notice dated 2082/03/11 (Nepali calendar) urging all citizens to register in the voter list immediately. The notice mentions that, according to Clause 4(2)(2) of the Voter List Act, 2073, voter registration will be stopped as soon as the election date is declared.
Hence, this is a final chance for anyone who missed earlier opportunities to register. The Commission has made a heartfelt appeal to all brothers and sisters across the country to take this opportunity seriously and get their names included in the voter list.
The Election Commission assures that the upcoming elections will be conducted fairly and freely, in line with its guiding principle:
“Free and Fair Election: Pride of the Nation.”
For more information or assistance, people can visit the official website of the Election Commission at www.election.gov.np or contact their office at Kantipath, Kathmandu.
Notice: Election Commission Preparing to Announce By-Election Date

Blogs
Birgunj Customs Office Collects Highest Revenue from Petroleum Imports

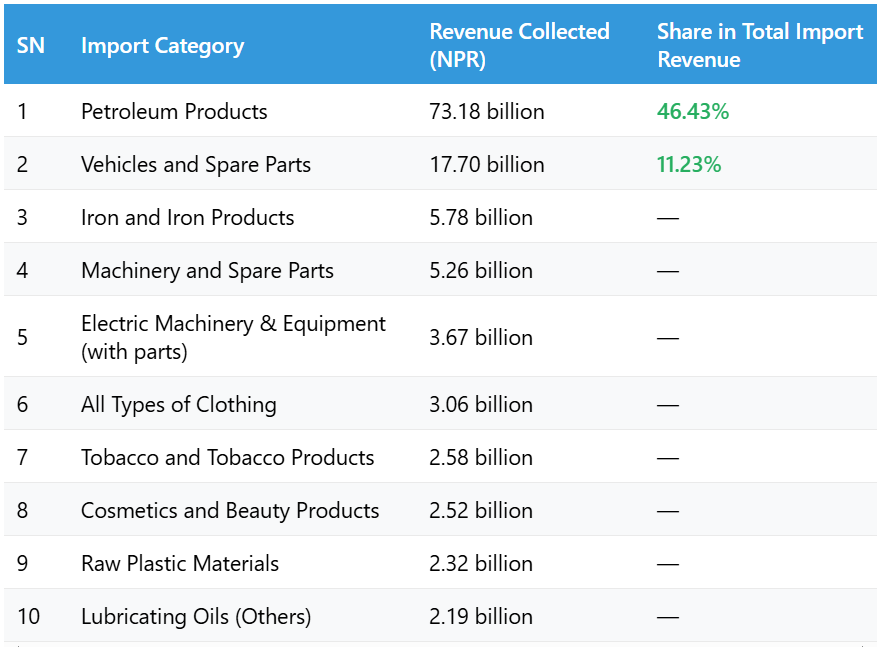
The Birgunj Customs Office has collected the highest revenue from the import of petroleum products in the first 11 months of the current fiscal year 2081/82. According to the office, a total of NPR 73.18 billion was collected in revenue from petroleum imports alone.
During this period, Nepal spent about NPR 174.09 billion to import five different types of petroleum products. These petroleum imports contributed 46.43% of the total revenue collected from the top 20 imported items, making it the most important source of income for the customs office.
Major Revenue Contributors from Imports
What Officials Say
Customs Chief Administrator Deepak Lamichhane stated that petroleum products and vehicle imports are the main sources of customs revenue at Birgunj. He highlighted that these two sectors consistently contribute the highest share of government income collected through imports.
Conclusion
The data from the Birgunj Customs Office shows that fuel and vehicles remain Nepal’s most heavily imported and taxed items. With more than 46% of the revenue coming from petroleum alone, any changes in fuel prices or import volumes can significantly affect national customs revenue.
-

 Blogs4 days ago
Blogs4 days agoPrivate Power Producers Protest ‘Take and Pay’ Provision in Budget
-

 Blogs1 year ago
Blogs1 year agoList of Stock Brokers in Nepal with NEPSE TMS Login – Updated
-

 Blogs4 days ago
Blogs4 days agoNepal Rastra Bank to Withdraw NPR 60 Billion from the Banking System on Monday
-
 Blogs1 week ago
Blogs1 week agoHydropower Gains 7.8% in One Month, Outperforming All Sectors
-

 Blogs4 days ago
Blogs4 days agoAsian Life Insurance to Issue Rights Shares from Asar 25
-

 Blogs3 months ago
Blogs3 months agoPure Energy IPO For General Public
-

 Blogs4 days ago
Blogs4 days ago52-Week Low & High Microfinance Shares in Nepal: Current Status and Future Outlook
-
Blogs1 year ago
Broker no. 58: Naasa Securities Co. Ltd.




